Sleep apnea is a serious medical condition that occurs as you sleep. When you sleep, your breathing stops multiple times throughout the night. This type of medical disorder is called a sleep disorder. In fact, sleep disorders affect approximately 50-70 million people nationwide. While sleep disorders are common, they can be incredibly dangerous if not treated.
Some cases of sleep apnea are mild. The symptoms include snoring or tiredness and fatigue. However, more severe cases of sleep apnea can cause heart problems or issues with your immune system. Over time, the strain on your heart can create more distressing side effects, such as a heart attack.
What Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea affects your breathing while you sleep. However, there are a couple of types of sleep apnea—obstructive, central, and complex.
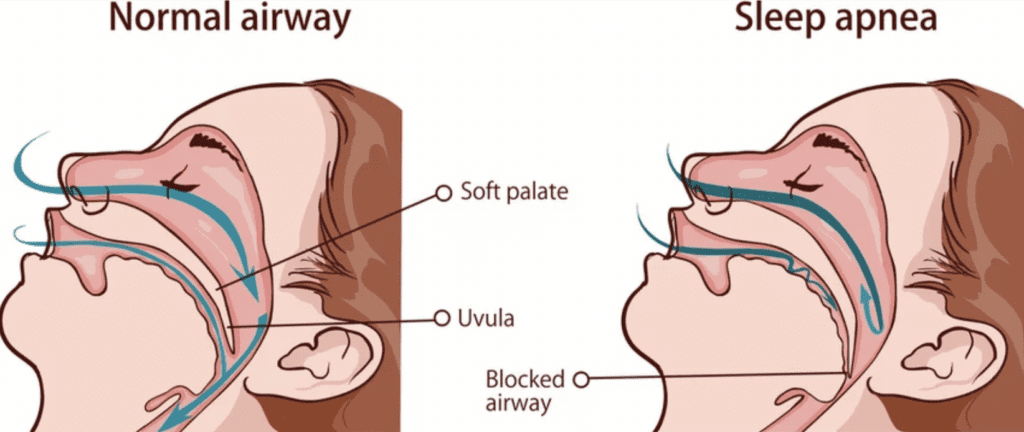
Obstructive sleep apnea is the most common form of sleep apnea. While you sleep, your muscles relax, including the soft tissues in your mouth and throat—soft palate, tongue, etc. With sleep apnea, these soft tissues will block your airway. An obstructed airway makes it difficult or impossible to breathe. Lack of oxygen reduces the oxygen levels in your blood.
So, your brain acts accordingly in order to keep you alive. Your brain rouses you from sleep so that you can breathe again. Generally, this waking time is so brief that you don’t remember it. This pattern of sleeping, not breathing, and waking can continue multiple times throughout the night.
Central sleep apnea is another form of sleep apnea that is less common. With central sleep apnea, your brain doesn’t send the right signals to your body. Meaning, your brain doesn’t tell the muscles in your chest and lungs to contract. Unfortunately, you forget to breathe for a short period of time. Like obstructive sleep apnea, your brain will rouse you to breathe again.
Complex sleep apnea is a type of sleep apnea that combines obstructive and central apnea.
Side Effects of Sleep Apnea
While there are many side effects of sleep apnea, some of them are more concerning than others.
The consistent drop in blood pressure and oxygen levels can create a strain on your heart. High blood pressure is common among patients with sleep apnea. Additionally, having obstructive sleep apnea increases your chances of having a heart attack or stroke. Your heart works overtime to pump more oxygen into your body when you stop breathing.
Then, once you wake suddenly, your heart speeds up and slows down rapidly. Your heart can only handle so much of this. In addition, repeated drops and increases in blood pressure and oxygen levels can increase your risk of sudden death.
Your immune system is another area that sleep apnea affects. Repeated waking and sleeping puts your body into a stressful state. When your body is stressed, it releases cortisol and adrenaline—stress hormones. Over time, your body can be overwhelmed by stress and reduce the effectiveness of your immune system. This can leave you more vulnerable to illnesses and infections.

